UK homeowners are on a mission to reduce household expenses and environmental impact. Solar panel battery storage systems have emerged as a popular solution, but finding the best system for your home can be a daunting task.

About the author: Steve Sparkes
Steve is a keen writer, mathematician and sportsman. An aeronautical engineer in a previous life, he has a passion for providing a truly exceptional customer experience. Steve oversees residential and single phase system design as the Renewables Manager at iJo Power.
In this comprehensive guide, discover how many panels and what size battery storage is needed to meet your energy requirements, as well as the cost of your ideal solar and battery setup. Find answers to all of your burning questions, from the nuts and bolts of solar installations to the intricacies of accreditation, planning laws and the retro-fitting of battery storage. Grab a cuppa and your reading specs if you’re in for the long haul, or navigate to the relevant section if time is of the essence.
Contents
I. Battery and Solar Panel Sizing
A. Determining your energy needs
B. Choosing the right battery capacity
C. Selecting the appropriate solar panel size
D. Inverters: types, size and capability
E. Importance of system sizing for efficiency
II. Solar System Purchasing and Government VAT Incentives
A. Solar panel planning permission considerations
C. Navigating UK government grants for solar panels
1. Feed-in Tariffs (FIT)
2. Smart Export Guarantee (SEG)
D. 0% VAT for domestic solar and battery systems
III. Choosing the Right Solar Panel Installer and Accreditations (in the UK)
A. Identifying reputable solar installers
B. Evaluating installer experience and customer reviews
C. Importance of industry accreditations
1. Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS)
2. Renewable Energy Consumer Code (RECC)
IV. Solar Panel and Battery Installation Process
A. Positioning your solar panels
1. Solar Panel Roof installation: on-roof and in-roof
2. Ground-mounted systems
3. Determining the optimal direction and angle
4. Pigeon proofing your solar panel system
C. Solar panels and battery installation alongside an air source heat pump
D. Retro-fitting battery storage to existing solar array
E. Safety considerations and local regulations
A. Regular inspections and cleaning
B. Monitoring system performance
C. Troubleshooting and maintenance tips
D. Planning for battery replacement
A. Can solar panels be used without battery storage?
B. Choosing the right battery manufacturer
C. Does the system still work in a power cut?
D. How long will the system work for in a power cut?
E. Do solar panels save money?
F. Can batteries be fitted to existing solar?
G. Do solar panels add value to my home?
I. Battery and Solar Panel Sizing
A. Determining your energy needs
Before you can select the right solar panel battery system for your home, it’s crucial to understand your household’s energy needs. To do this, follow these steps:
- Review your energy bills: Start by gathering your energy bills for the past year. These bills should provide information on your energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Add up the total energy usage for the year and divide by 12 to calculate your average monthly energy consumption.
- Account for seasonal fluctuations: Keep in mind that your energy usage may fluctuate seasonally due to factors such as changes in daylight hours, weather patterns, and the use of heating or cooling systems. Be sure to consider these changes when determining your overall energy requirements. You can identify seasonal trends by comparing your energy consumption month by month.
- Consider your lifestyle and habits: Think about how your daily habits and routines may affect your energy consumption. For example, if your family spends more time at home during weekends or holidays, your energy usage may be higher during these periods. Additionally, the use of energy-intensive appliances, such as electric ovens, washing machines, and tumble dryers, can have a significant impact on your energy consumption.
- Energy efficiency improvements: Finally, evaluate your home’s energy efficiency and identify areas where you can make improvements. This might include upgrading insulation, installing double or triple-glazed windows, or replacing older appliances with energy efficient models. By making these improvements, you can reduce your overall energy consumption and the size of the solar panel battery system you’ll need.
Future energy needs: When calculating your energy needs, it’s essential to consider any changes that may occur in the future. For example, if you plan to buy an electric vehicle, install a home office, or add more family members to your household, your energy consumption is likely to increase. Be sure to factor in these changes when determining your overall energy requirements.
NSN work alongside iJo Power, providing EV car charging installations alongside solar and battery storage systems.

By taking the time to accurately assess your household’s energy needs, you’ll be better prepared to choose a solar panel battery system that meets your requirements and maximizes cost savings and environmental benefits.
B. Choosing the right battery capacity
Once you know your energy needs, it’s time to choose the appropriate solar battery storage capacity. Solar batteries are rated in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which represents the amount of energy they can store. To select the right battery capacity for your home, follow these steps:
- Determine your daily energy usage: Calculate your average daily energy consumption by dividing your monthly energy usage by the number of days in a month. This will give you an estimate of the amount of energy you use each day.
- Charge and discharge rate: Different batteries deliver energy at different rates (known as power). High load items such as tumble driers and electric heating require high power. As well as the total usable capacity of a battery, it is important to determine whether it will be able to meet your power requirements at specific times of the day. Battery datasheets will contain this information, but speak to an iJo Power expert if you are not sure.
As well as battery sizing, consider charge and discharge rates to make sure the battery can meet the electrical demands of your household.
Read the specification carefully, or speak to an expert.
- Estimate backup power requirements: Think about how much energy you want to store for use during periods of low sunlight or power outages. Consider your essential energy needs during these times, such as lighting, heating, cooling, and powering critical appliances like refrigerators and communication devices.
- Calculate battery capacity: To answer the question of “what size solar battery do I need?” you should aim for a battery capacity that covers your essential energy needs during periods of low sunlight or power outages. Multiply your daily energy usage by the number of days you want to have backup power available. This will give you a rough estimate of the minimum battery capacity you’ll need.
- Consider battery efficiency and depth of discharge (DoD): Keep in mind that batteries have varying levels of efficiency and depths of discharge. A battery’s efficiency refers to the percentage of energy that can be used compared to the total stored energy. Depth of discharge (DoD) refers to how much of a battery’s capacity can be used before it needs to be recharged. When selecting a solar battery, look for one with a high efficiency and a suitable DoD to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Factor in battery lifespan: Solar batteries have a limited lifespan, and their capacity typically decreases over time. When choosing a battery, consider its expected lifespan and how it may affect your energy storage needs in the long run. It’s essential to select a battery with a proven track record of reliability and durability to ensure that your investment is worthwhile.
Calculate the usable storage of a battery for accurate comparisons.
Depth of Discharge (%) x Stated Capacity (kWh) = Usable Capacity
Hit play on the animation above. The size of each dot represents the total cycled capacity of that battery, assuming a full charge and discharge each day.
Each battery is warranted for 10 years (7 years with a free 3 year extension for the Pylontech). Factoring in DoD and initial cost for each, we can see the real terms cost per kWh charged and discharged during the life cycle of the battery. While GivEnergy, Pylontech and Growatt batteries complete their warranted 10 year life cycle with an approximate cost of 11p/kWh, the Tesla Powerwall 2 is just over double at 23p/kWh. It is worth noting that all of these batteries are modular and can be installed in multiples to create a larger overall storage capacity.
By taking these factors into account, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right solar panel battery capacity for your home, ensuring you have sufficient backup power during periods of low sunlight or power outages.
C. Selecting the appropriate solar panel size
In addition to choosing the right battery capacity, you’ll also need to determine how many solar panels are required to power your home. Here are the key factors to consider when selecting the appropriate solar panel size:
- Assess your roof size and orientation: The available space on your roof will dictate how many solar panels you can install. Measure your roof’s dimensions and consider the orientation of the panels. Ideally, solar panels should face south in the UK to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day, but East and West facing arrays can also provide excellent solar generation. Keep in mind that obstructions such as chimneys, vents, and shading from trees or neighbouring buildings can also impact the efficiency of your solar panels.
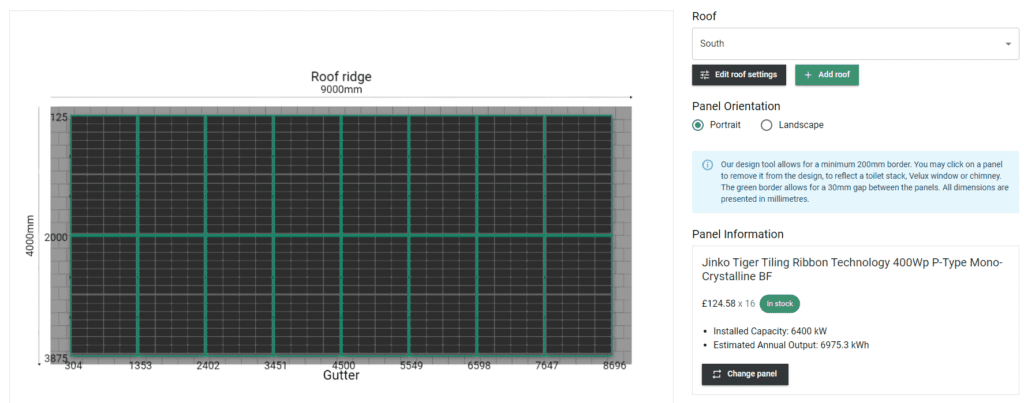
- Solar panel mounting: On-roof or in-roof mounting impacts the choice of solar panels available to you. On-roof systems are usually compatible with larger output panels when compared with in-roof.
- Understand solar panel efficiency: Solar panel efficiency refers to the percentage of sunlight that is converted into electricity. Higher efficiency panels can generate more electricity using less space. When comparing solar panels, consider their efficiency ratings to ensure you’re getting the most power output for your available roof space.
- Estimate your location’s solar potential: The amount of sunlight your location receives plays a significant role in determining the number of solar panels needed. The UK, for instance, receives varying amounts of sunlight depending on the region and time of year. You can use tools such as the UK Solar Energy Resource Maps or consult local meteorological data to estimate the solar potential in your area.
Suitably qualified system designers, such as iJo Power, provide clear and accurate generation data according to your location, roof orientation, inclination and array size.
- Calculate the required solar panel output: Divide your average daily energy usage (calculated in section A) by the average daily sunlight hours in your location. This will give you an estimate of the total solar panel output needed to cover your energy needs.
- Determine the number of solar panels: Divide the required solar panel output by the output of a single solar panel (measured in watts) to determine the number of panels needed. Consider using high-efficiency solar panels to reduce the total number of panels required and make better use of your available roof space.
- Consult with a professional solar installer: To ensure accuracy and optimal system performance, it’s always best to consult with a professional solar installer. At iJo Power, we provide our customers with a thorough breakdown of the expected generation of solar array designs throughout the year, to ensure a good coverage of expected usage.
Making best use of your space: You may be concerned that your property does not have sufficient space for your required number of solar panels. Solar experts, like iJo Power, are often aware of ways to increase your solar capacity by finding ways to include more panels and increase efficiency by using different mounting systems, orientations or bespoke solutions.
By taking all of these factors into account, you’ll be able to answer the question of “how many solar panels to power a house?” and choose the appropriate solar panel size for your home. Properly sizing your solar panel system will help you maximize energy production, reduce your reliance on grid electricity, and save money on your energy bills.
D. Inverters: types, size and capability
One of the most common misconceptions in the world of solar and battery storage is that of the inverter. Not all inverters are created equal.
The inverter is the brains of the operation, deciding what goes where, at what rate, and for how long. There are several types of inverter, and it is important to have at least a basic understanding of what is best suited to your needs.
Not all inverters are created equal. Check the specification carefully or speak to a technical expert to make sure that your chosen inverter will do exactly what you think it says on the tin.
Hybrid inverters: Increasingly becoming the go-to option for many residential settings, the hybrid inverter is compatible with solar and battery storage systems. Household loads are met either by solar generation, battery power, and topped up by grid import when necessary. Excess solar generation is directed to batteries or exported to the grid.
Most can function with or without solar and with or without battery storage, providing the flexibility to add to an existing system at a later date. Hybrid inverters often (but not always) provide EPS (emergency power supply) in the event of a power cut.
Be sure to gain a clear understanding of the performance capability of your hybrid inverter. In many cases, the power that can be delivered from the solar panels to the household loads exceeds the power that can be drawn from the batteries. For example, a 6kW rated inverter may be able to provide solar power of 6kW to meet the household requirements, but it may harness up to 7.5kW, directing the extra 1.5kW to battery storage. At night time, it may only be able to provide a maximum of 4kW of power from the batteries to the household loads, despite the 6kW rating..
Grid tied inverters: These act as a see-saw, directing generated solar power to the household loads when required, or exporting to the grid. Excess energy cannot be stored in batteries. These are the simplest and cheapest inverters, although data suggests that less than 40% of generated energy is actually consumed by the household. Grid tied inverters are common on older installations which benefitted from favourable feed in tariffs, but are largely being overtaken by the hybrid inverter.
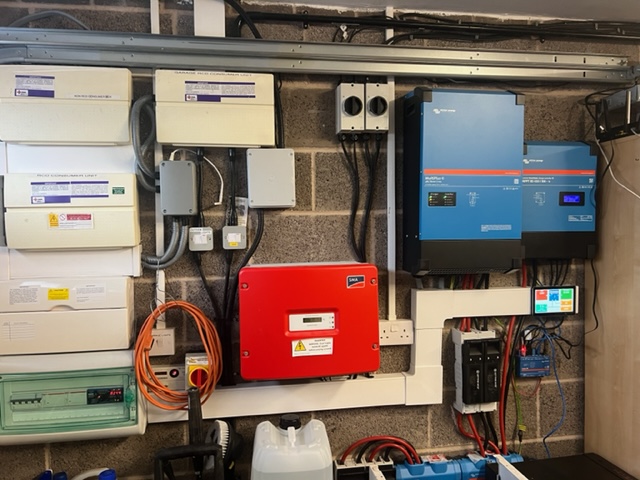

AC coupled: AC coupled inverters are added to an existing grid tied system in order to introduce battery storage. This results in two inverters running simultaneously, with the expected additional overall cost. There are greater conversion losses due to multiple conversions between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). The additional AC coupled inverter must at least match the performance capability of the grid tied inverter.
DC coupled: Solar panels and most battery storage systems work in DC (direct current) whilst household loads are drawn in AC (alternating current). A DC coupled system minimises conversion losses by transferring excess solar generation straight to storage. Usually, inverters for DC coupled systems do exactly what they say on the tin: the continuous power rating is what can be delivered from the panels to your home, and matches that which can be sent to and from the batteries.
The bottom line: Speak to your system designer to ensure that you are fully aware of the capability of your inverter before proceeding, to avoid future disappointment.
E. Importance of system sizing for efficiency
Properly sizing your solar panel and battery system is essential for maximizing energy efficiency and cost savings. To understand the significance of accurate system sizing, let’s explore the potential issues associated with undersized and oversized systems:
Undersized system:
Insufficient energy production: An undersized solar panel system may not produce enough electricity to meet your energy needs, leading to increased dependence on grid electricity and higher energy bills.
Frequent battery depletion: If your battery capacity is too low, it may not store enough energy to cover your usage during periods of low sunlight or power outages, resulting in a lack of backup power when needed.
Increased system wear and tear: An undersized system may be forced to operate at full capacity more frequently, which can cause components to wear out more quickly and require more maintenance or replacement.
Oversized system:

Wasted energy: An oversized solar panel system may generate more electricity than you can use or store, leading to wasted energy.
Higher initial costs: Installing a larger-than-necessary solar panel and battery system comes with increased upfront costs for equipment and installation. As nice as it might be to install the biggest system possible, the reality is that most are constrained by a budget, and need to see healthy returns on investment to warrant the expenditure.
Limited additional benefits: While an oversized system may provide some extra backup power during periods of low sunlight, the additional benefits may not justify the higher costs, especially if your grid electricity rates are relatively low.
Optimising returns: Exporting more energy to the grid than necessary may see your returns dwindling. Whilst favourable export tariffs are available, it is important to strike the right balance so that the best return on investment and future savings are achieved.
To ensure your solar panel and battery system is sized correctly, follow these guidelines:
Accurately assess your energy needs: As mentioned in section A, determine your average daily energy consumption and consider any future changes in energy usage.
Choose the appropriate battery capacity: Based on your energy needs and desired backup power duration, select a battery capacity that provides adequate storage without being excessive, as discussed in section B. Choosing a system which allows you to increase your battery storage in the future is a good way to avoid initial over-spend.
Determine the optimal number of solar panels: Calculate the required solar panel output and choose the right number of solar panels to meet your energy needs, as outlined in section C.
An oversized system leaves you out of pocket with a break-even point all but a tiny dot on the horizon.
Consult with a professional solar installer: Work with a reputable solar installer like iJo Power to conduct a thorough assessment of your home, location, and energy needs, and provide expert guidance on the right system size for your situation.
By carefully considering your energy needs, battery capacity, and the number of solar panels required, you’ll be well on your way to a more sustainable and cost-effective home energy solution. A properly sized solar panel and battery system will help you achieve the greatest energy efficiency, reduce your reliance on grid electricity, and save money on your energy bills in the long run.
II. Solar System Purchasing and Government VAT incentives (UK only)
A. Planning Permission considerations
Before installing a solar panel system on your property, it’s essential to check if you require planning permission. In most cases, solar panels are considered ‘permitted development’ in the UK, meaning that planning permission is not necessary. However, there are some exceptions and guidelines you need to be aware of:
- Listed buildings and conservation areas: If your property is a listed building or located within a conservation area, you may need to obtain planning permission before installing solar panels. In these cases, it’s crucial to consult your local planning authority for guidance on planning permission requirements specific to your property.
- Roof alterations and solar panel placement: For most residential properties, solar panels can be installed without planning permission as long as they don’t protrude more than 200mm from the roof slope and don’t extend above the highest part of the roof (excluding the chimney). If your proposed installation does not meet these criteria, you may need to apply for planning permission.

- Ground-mounted solar panels: If you’re considering a ground-mounted solar panel system, you’ll need to ensure it doesn’t exceed a certain size or height and is within a specific distance from your property’s boundaries. Check with your local planning authority for specific requirements in your area.
- Building regulations: Although planning permission may not be required, your solar panel installation must still comply with UK building regulations. This includes ensuring that the installation is structurally sound, safe, and carried out by a qualified installer.
- Neighbours and potential objections: Although not a legal requirement, it’s a good idea to inform your neighbours about your solar panel installation plans, particularly if the panels may affect their view or sunlight. Open communication can help address any concerns and avoid potential objections during the planning permission process.
By considering these factors and consulting with your local planning authority, you can ensure that your solar panel installation complies with planning permission requirements and avoid potential issues down the line. Proper planning and adherence to regulations are crucial for a successful and hassle-free solar panel project.
B. Understanding your budget
When considering a solar panel battery system, it’s essential to understand your budget and the costs involved. To help you plan effectively, here’s a breakdown of the various expenses you may need to account for:
- Solar panel costs: The price of solar panels varies based on factors such as their efficiency, output capacity, and the manufacturer. Research different brands and types of solar panels to find the best quality and price for your needs. Speaking to system designers and installers, such as iJo Power, is a good way to gain an understanding of which manufacturers are recommended, and why.
- Battery storage costs: Similar to solar panels, the cost of solar battery storage depends on factors such as capacity, technology, and the manufacturer. Investigate different battery options to determine the best fit for your energy needs and budget.
- Installation fees: Installation costs can vary depending on the complexity of your project, your location, and the installer’s expertise. Obtain multiple quotes from reputable solar installers like iJo Power to ensure you receive a fair and competitive price.
Costs, more costs, and then some hidden costs. To avoid overlooking the critical costs of your solar and battery storage project, try an online calculator to get a good starting point.
- Permits and inspections: While many solar panel installations do not require planning permission, you may still need to budget for building regulation compliance fees or other permits if your property falls under certain exceptions. Research your local planning authority’s guidelines to account for any potential fees.
- Maintenance and monitoring: Although solar panels and batteries generally require minimal maintenance, it’s essential to budget for potential maintenance costs, such as inverter replacements, or periodic system check-ups to ensure optimal performance.
- Insurance and warranties: Some solar panel and battery manufacturers offer extended warranties, which can add to the initial cost but provide peace of mind and protection for your investment. Additionally, you may need to update your home insurance policy to cover your solar panel system, which could result in a premium increase.

To help you estimate the overall cost of your solar project, you can use online cost calculators or seek quotes from professional solar installers like iJo Power. By carefully evaluating your budget and taking into account all potential expenses, you can make informed decisions about the most cost-effective solar panel and battery system for your home.
C. Navigating UK incentives and government grants for solar panels and battery storage
The UK government offers various incentives and government grants for solar panels in the UK to encourage the adoption of renewable energy. Some of the key programs include:
- Feed-in Tariffs (FIT): The FIT scheme, which has now been phased out, provided payments to households generating their own electricity through renewable energy sources like solar panels. Although the FIT scheme is now closed to new applicants, existing participants will continue to receive FIT payments for the remainder of their contract.
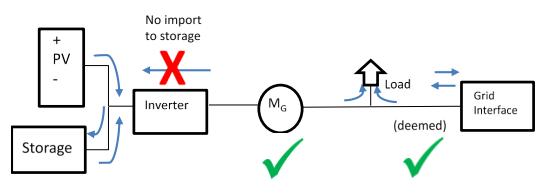
Ofgem have provided detailed technical guidance for those wishing to add battery storage to existing solar installations that currently benefit from historic feed in tariffs. There are many scenarios to consider regarding wiring configurations and locations of meters, so it is worth seeking expert advice from technical experts such as iJo Power to ensure that you are not in breach of your FIT agreement. More on this in section IV.D.
- Smart Export Guarantee (SEG): Replacing the FIT scheme, the SEG requires energy suppliers to pay households for any surplus electricity generated by their solar panels and exported to the grid. The rates and terms of SEG payments vary between suppliers, so it’s crucial to compare offers before signing up. The stipulation for SEG payments is that they are ‘above 0p/kWh’ so payments are typically low.
- Export tariffs: Many energy suppliers now offer their existing customers more attractive export rates. Fixed rates typically range from 7p-15p/kWh. More creative tariffs are also available which offer different import and export rates at different times of day, several of which are aimed at either electric vehicle or home batter owners. Whilst Octopus are often cited as leading the way in this area, other suppliers are in hot pursuit.





It is worth considering the benefits and drawbacks of different tariffs as you plan for your solar and battery system. At iJo Power, we provide all customers with projections for return on investment and future savings based on their chosen energy provider, import and export tariff. We can also carry out comparisons of different tariffs, making the decision making process that bit easier.
D. 0% VAT for domestic solar and battery systems
The high cost of electricity has been a significant factor in the recent surge in domestic and commercial solar panel and battery storage installations. Recognising the importance of solar energy to achieve the UK Government’s net zero target, Rishi Sunak announced in April 2022 that there would be 0% VAT to pay on all solar and associated equipment and installation costs for the following five years.
Pay for your solar panels and battery storage equipment and installation through a UK VAT registered installer and you benefit from 0% VAT on the whole lot – several thousand pounds in most cases.
Put simply, until 2027, the cost of solar panel and battery storage systems is 20% less than normal. Equipment must be purchased and installed by a VAT registered installer in order to gain from this incentive. With the cost of producing 1MWh from solar reducing by 89% since 2009, solar and battery storage are currently more affordable than ever before.
III. Choosing the Right Solar Panel Installer and Accreditations (in the UK)
A. Identifying reputable solar installers
Selecting a qualified and experienced solar panel and battery installer is crucial for a successful installation. To ensure you choose the best installer for your needs, consider the following steps to identify reputable companies in your area:
- Recommendations: Ask friends, family, neighbours, or co-workers who have installed solar panels for recommendations. Personal referrals can provide valuable insights into the quality of work and customer service provided by a solar panel and battery installer, as well as lessons learnt along the way.
- Online research: Search engines to look for companies that specialise in solar panel installations in your area, and pay attention to their website quality, services offered, and expertise.
- Local directories: Browse local business directories and trade associations which usually provide contact information, a brief overview of the company, and sometimes customer reviews.
- Portfolio and case studies: Reputable solar installers should have a strong portfolio of completed projects, showcasing their experience and expertise. Look for case studies on their website or request examples of previous solar panel and battery installations that are similar to your project.
- Testimonials and reviews: Check online review platforms, such as Google Reviews, Trustpilot, or social media, to read testimonials from previous customers. These reviews can provide insight into the installer’s professionalism, work quality, and customer satisfaction.

- Initial consultation: Contact suitable installers to discuss your project and gauge their level of expertise and knowledge in the field. A reputable installer should understand the pros and cons of different equipment manufacturers and systems and be able to answer your questions, provide guidance, and offer a detailed quote for your solar panel and battery system.
B. Evaluating installer experience and customer reviews
Before choosing a solar panel battery installer, it’s essential to assess their experience and expertise to ensure they can successfully complete your project. Here are some steps to help you evaluate the experience and customer satisfaction of potential solar panel installers:
- Years in business: Consider the number of years the installer has been in the solar industry. A company with a longer track record will have more experience and knowledge in solar panel and battery system installations.
- Completed installations: Enquire about the number of installations the company has completed, particularly with solar panel and battery systems similar to yours. A higher number of installations can indicate a greater level of expertise.
- Certifications and training: Check if the installer holds relevant certifications and has undergone specialised training in solar panel and battery system installation. This can help ensure they are up to date with industry best practices and safety guidelines.
- Customer reviews and testimonials: Read customer reviews and testimonials on various platforms, such as Google Reviews, Trustpilot, social media, and the installer’s website. Pay attention to comments about the installer’s professionalism, quality of work, communication, and problem-solving abilities.
- Case studies and references: Request case studies or references from previous clients who have had similar solar panel and battery system installations. This can provide valuable insights into the installer’s ability to handle your specific project requirements.
- Awards and recognitions: Find out if the solar panel installer has received any industry awards or recognitions for their work. This can be an indicator of their commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction.
- Consultation and communication: Gauge the installer’s communication skills and willingness to answer your questions during the initial consultation. A reputable solar panel installer should be transparent, informative, and responsive throughout the entire installation process. A company that doesn’t take time to answer your questions and address any concerns during the consultation stage is unlikely to be easily contactable later on in the process.
- Budget vs performance: Make sure that your chosen installer will consider your personal energy requirements in their system designs. Whilst there may be higher performance systems available, your design and installation should be designed and carried out to provide you with the best possible returns on your investment, and this doesn’t always mean the largest system is best. Your installer should be happy to answer questions on the performance and expected returns on your system, to ensure that it is right for you.
If your design and installation team don’t ask for your energy consumption data, it’s a red flag that your quoted system is not specifically designed to meet your needs.
- Unforeseen circumstances: Solar panel and battery installation is a process that is unique to each customer and each property. As a result, it is possible that unforeseen problems can arise during installation. You need to be confident that your chosen installer will be contactable and helpful in resolving any issues along the way.
By thoroughly evaluating the experience and customer satisfaction of potential solar panel installers, you can make an informed decision, choosing a company that has a history of positive feedback and successful installations.
C. Importance of industry accreditations
When choosing a solar panel installer, it’s vital to verify their industry accreditations to ensure a successful installation that meets specific quality and safety standards. These certifications also play a role in eligibility for government incentives as well as export tariffs from energy suppliers. The key accreditations to look for include:
- Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS): The MCS is a nationally recognised certification scheme for renewable energy technologies, including solar panels. An MCS certificate for solar panels serves as proof that the installer and the products they use meet rigorous quality, performance, and safety standards. By choosing an MCS-accredited installer, you can be confident that your solar panel and battery system will be installed correctly and perform as expected.


- Renewable Energy Consumer Code (RECC): The RECC is a consumer protection scheme that ensures solar panel installers adhere to a strict code of conduct. Membership in the RECC demonstrates a commitment to high-quality customer service and ethical business practices. When you choose an installer who is a member of the RECC, you can expect transparency, fair pricing, and excellent communication throughout the installation process.
In addition to these key accreditations, you may also want to consider other industry certifications and memberships, such as NAPIT (National Association of Professional Inspectors and Testers) or HIES (Home Insulation and Energy Systems Contractors Scheme), which can further demonstrate a solar panel installer’s commitment to industry standards and best practices.
Ask your installer about G98 notification or G99 application if you are not sure.
If they aren’t sure, find someone who is.
Your installer will need to complete and provide documentation as well as commission your system. This may involve an application to the Distribution Network Operator for G99 approval if your inverter rating is greater than 3.68kW.
Your system will almost certainly need to be connected to a monitoring and management platform, so that you can monitor performance and manage your inverter to oversee import and export windows. Ensure that your chosen installer has the expertise and capability to complete any necessary applications, paperwork and commissioning tasks with confidence and in a timely manner.
All necessary paperwork and applications are taken care of by iJo Power as part of the commitment to excellent customer service. This includes obtaining necessary permits and industry accreditations to providing comprehensive guidance and support throughout the installation process, ensuring a seamless solar panel and battery system implementation for your home.
It’s by no means a pre-requisite of the solar industry, but a company looking to redefine the quality of experiences of customers within the industry, we wanted to make a commitment that goes above and beyond. We’re proud to be B-Corp Accredited.

Section IV: Solar Panel Battery Installation Process
Installing solar panels and batteries in your home can be a daunting process, but with the right information, guidance and preparation, it can be simple and straightforward. In this section, we will discuss the installation process for solar panels and batteries and the different factors you need to consider to ensure a successful installation.
A. Positioning your solar panels
- Solar Panel Roof installation: Maximising light and minimising shade makes roofs the ideal location for solar panels if space allows. It is important to ensure that your roof is strong enough to support the weight of the solar panels and that it is in good condition before installation. Shading on some panels will affect all of the panels connected to the same string. In this case, individual panel optimisers may help to address any imbalance. If your roof is not suitable, you can consider ground-mounted systems.

- Ground mounted systems: Ground mounted solar panels are an excellent alternative to roof-mounted systems. Where roof space is limited or orientated away from sunlight, ground mounts provide a straightforward and easily accessible means of installing solar panels. These systems are well suited to larger gardens or fields, where shading from trees, buildings or hedges is not an issue. The ground mount can be orientated to maximise exposure to sunlight.
Advances in solar panel optimisers have opened up even the most challenging roof surfaces for solar generation.
- Determine the optimal direction and angle: The direction and angle of your solar panels can greatly affect their energy output. It is important to determine the optimal position for your solar panels to maximize energy generation. This is usually south-facing in the UK, but other factors such as shading need to be considered. East-West split arrays can be very effective, and mounting systems for flat roofs have been developed in order to optimise the generation from the available space.
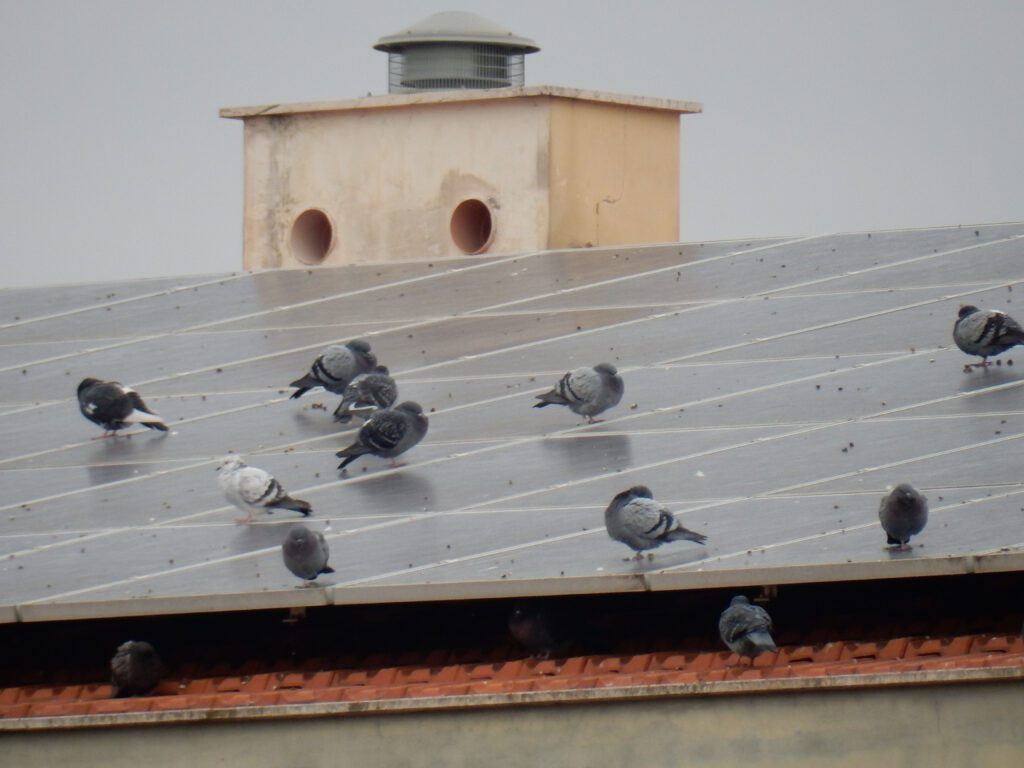
- Pigeon proofing your solar panel system: Pigeons and other birds can cause damage to your solar panels and affect their energy output. Cabling can be dislodged or damaged by nesting and sheltering birds, while birds mess can affect the solar generation of panels. It is advised to install pigeon-proofing measures to keep birds away from your solar panels.

B. Positioning your battery
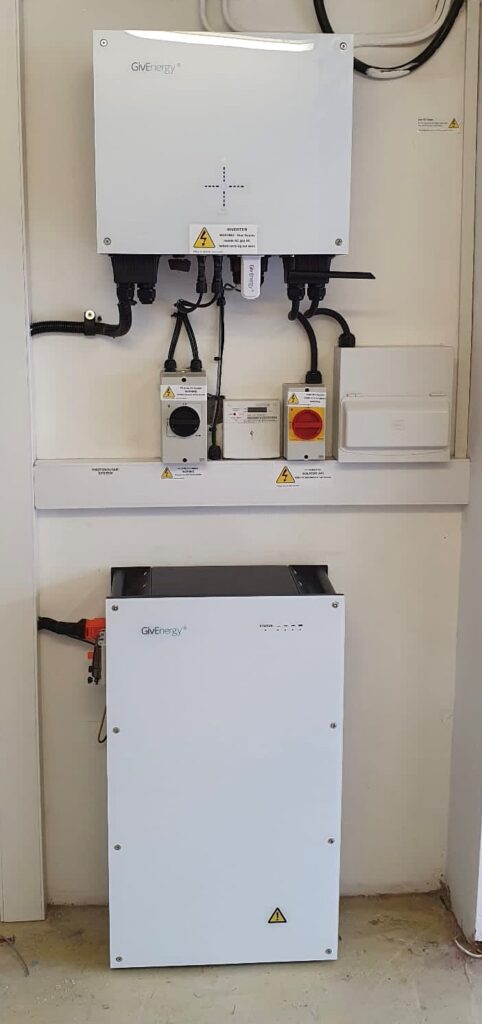

When choosing a location for your battery, there are a few things to consider. Firstly, the battery should be installed in a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and monitoring. It is important to choose a location that is dry, well-ventilated, and away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Whilst some batteries are designed to cope with external conditions, internal installation is often best to ensure moderate temperatures and protection from the elements. Electrical equipment, including inverters and batteries, should be mounted on fire retardant materials.
Secondly, it is important to consider the size and weight of the battery. Large batteries can be heavy, and it is important to ensure that the chosen location is capable of supporting the weight of the battery. Your installer should be able to advise you on the best location for your battery based on your home’s specific requirements.
This GivEnergy Gen2 installation by iJo Power’s Midlands-based partners MCI Electrical Ltd highlights the sensible location of the battery below the inverter, with equipment and components suitably spaced to allow for access and airflow.
C. Solar panels and battery storage alongside an air source heat pump
Environmental benefits play a key part in motivating home owners to adopt solar panels and battery storage. Using your solar energy storage solution to power an air source heat pump is another way of reducing your carbon footprint, as clean energy can be used to heat your home and water.
Air source heat pumps can be 300-400% efficient, meaning that every kWh of energy used provides 3-4kWh of heat. While central heating is typically used in the evenings when solar generation is at a minimum, energy stored in batteries can then be used to provide heating and hot water.
Solar panels and battery storage fitted alongside an air source heat pump can see your reliance on imported energy reduce dramatically, along with your utility bills and your carbon footprint.
Air source heat pumps work very well with wet underfloor heating and hot water cylinders, whilst it is advised to insulate homes well to ensure the highest efficiencies. Airsource heat pumps call for significant energy during winter months, and therefore it is advisable to establish your daily usage in order to size your battery storage correctly.
D. Retrofitting battery storage to existing solar panels
Many homes were fitted with solar panels before the relatively recent advances in home battery technology. In many cases, homeowners benefit from Feed In Tariffs with several years remaining on contracts. Whilst different payment terms exist, deemed export is commonplace, whereby payments are made based on 50% of the generation of the solar panels.
You may be in this situation yourself and looking to add battery storage to your system. Of course, this would enable you to capture and make use of a far higher percentage of your generated solar energy, but it is essential to ensure that this does not breach the terms of your FIT contract. Ofgem has produced extensive guidance on the topic of co-location of battery storage facilities alongside existing solar installations, but it requires a certain level of technical expertise and in many cases the careful configuration of the system including the correct positioning of generation meters or bi-directional meters.
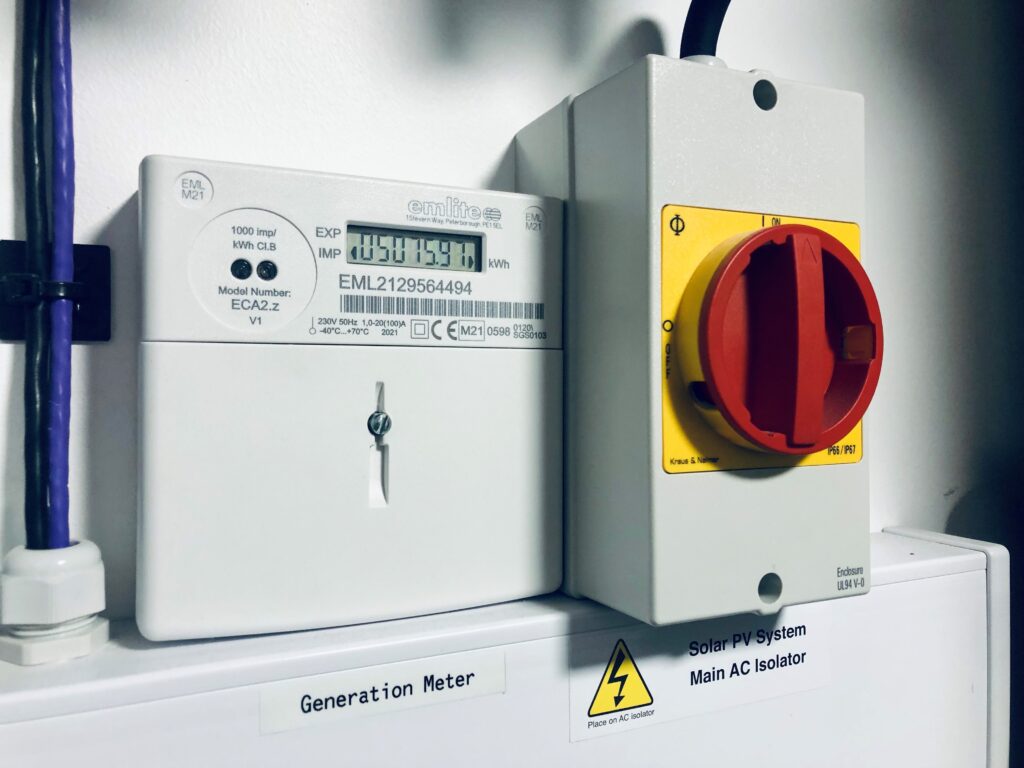

Positioning is everything: Get your generation or bi-directional meters in the right place and you can benefit from battery storage and keep your existing FIT payments.
If in doubt, contact a reputable installer such as iJo Power to discuss your options, or for a design of a compliant system.
E. Safety considerations and local regulations
Installing solar panels and batteries can be a complex process, and it is important to ensure that you comply with local regulations and safety guidelines. In the UK, accredited installers of the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) are recommended to ensure work is quality assured.
When choosing an installer, it is important to ensure that they are MCS certified and have the necessary qualifications and experience to carry out the installation safely and efficiently. Your installer should also be able to advise you on any local regulations or planning permission requirements that may apply to your installation.
It is important to follow all safety guidelines and instructions when installing solar panels and batteries. Your installer should provide you with comprehensive safety information and advice on how to maintain and monitor your system to ensure its ongoing safety and efficiency.
V: Ongoing Maintenance
Maintaining your solar panel battery system is crucial to ensuring its longevity and efficiency. In this section, we will discuss the ongoing maintenance requirements for your solar panel and battery system and offer some tips on how to keep it running smoothly.
A. Regular inspections and cleaning
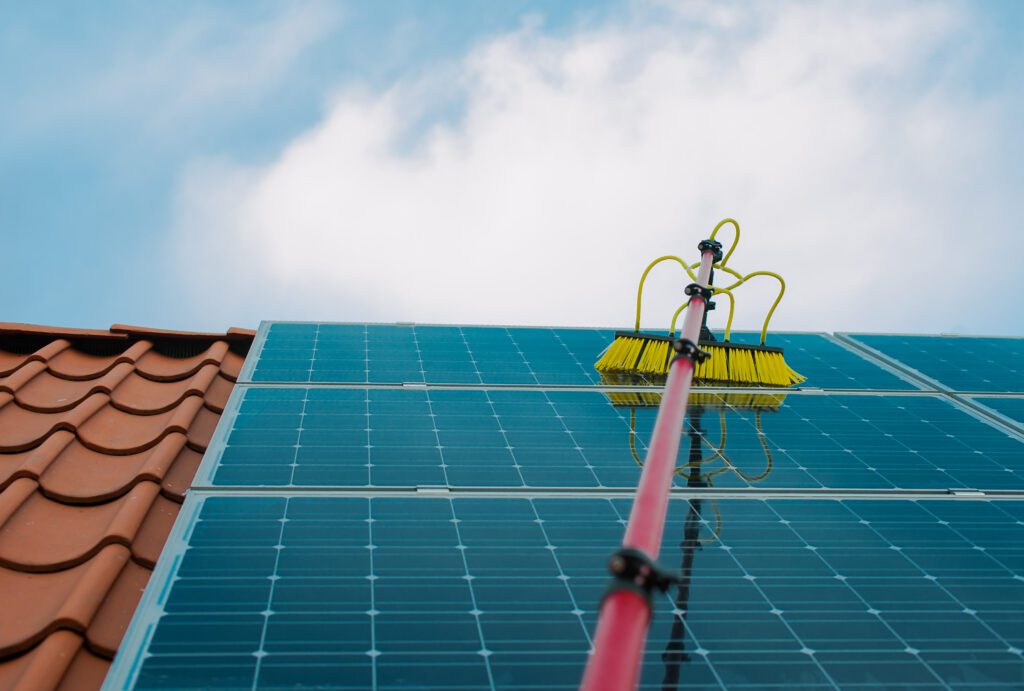
Regular inspections and cleaning are necessary to ensure that your solar panel system is operating at maximum efficiency. Solar panels are designed to self-clean with regular rainfall, and should perform well for many years. It is recommended to clean panels at least once per year. Professional window cleaners possess the equipment and skills needed for high level cleaning.

B. Monitoring system performance
Monitoring the performance of your solar panel and battery system is essential to ensuring that it is running efficiently. Many systems come with monitoring software that allows you to track your energy generation and usage. It is important to regularly check the performance of your system to identify any potential issues or inefficiencies.
If you notice any significant drops in energy generation, contact your installer or a qualified professional to investigate and rectify the issue.
Make sure your solar and battery storage installation team provide you with access to a monitoring portal or app.
Apps such as Maximisemy.energy can automate your system import and exports to increase your savings.
It is likely that your installer will introduce you to the equipment manufacturer’s monitoring portal. This may allow you to manually control the import and export of energy to and from the grid.
It is also worth exploring the benefits of automated system management, such as Maximisemy.energy. This saves time and money by automatically importing and exporting the correct amount of energy and making use of off-peak tariffs, alongside accurate solar forecasting for the coming day.
C. Troubleshooting and maintenance tips
Despite regular maintenance, issues may arise with your solar panel and battery system. It is important to have a basic understanding of the system and some troubleshooting tips to help you identify and potentially fix any issues.
Some common issues with solar panel systems include faulty wiring, damaged panels, and battery failure. If you are unsure of how to troubleshoot these issues, contact a qualified professional for assistance.
D. Planning for battery replacement
The battery is a crucial component of your solar panel and battery system, and it will eventually need to be replaced. The lifespan of a battery will depend on a variety of factors, including its composition, the size of the battery, the frequency of use, and the manufacturer’s specifications.
It is recommended that you plan for battery replacement in advance and budget for the cost of a new battery. Your installer should be able to advise you on the expected lifespan of your battery and when you should plan for replacement.
In conclusion, ongoing maintenance is essential to ensuring that your solar panel and battery system operates efficiently and lasts for many years. Regular inspections and cleaning, monitoring system performance, troubleshooting and maintenance tips, and planning for battery replacement are all important aspects of maintaining your system. With proper maintenance, you can enjoy the many benefits of renewable energy while reducing your environmental impact and saving money on energy bills.
VI: Q&A
In this section, we will answer some of the most commonly asked questions about solar panel and battery systems.
A. Can solar panels be used without battery storage?
Yes, solar panels can be used without a battery. In this configuration, excess energy generated by the solar panels is fed back into the grid. This is called a grid-tied system. However, if you want to store excess energy for use during periods of low sunlight or power cuts, a battery is required. Different types of inverters are used for different arrangements, and it is not always straightforward to add battery storage at a later date without purchasing an additional or replacement inverter.
B. Choosing the right battery manufacturer
Choosing the right battery manufacturer is an important decision when installing a solar panel and battery system. It is important to choose a reputable manufacturer with a track record of producing high-quality batteries. Your installer should be able to recommend a manufacturer and provide you with information on their battery’s performance and reliability.
C. Does the system still work in a power cut?
Yes, some solar panel and battery systems can still work during a power cut. In fact, this is one of the main advantages of having a battery backup. When the grid goes down, your battery will kick in and provide power to your home. This means that you can continue to use your essential appliances and stay connected during a power cut.
However, not all systems provide back-up power in the event of a power cut. It is important to discuss this with your installer to ensure that your chosen equipment and wiring configuration provides this feature if required.
D. How long will the system work for in a power cut?
Where this capability is provided, the length of time your solar panel and battery system will work during a power cut will depend on the size of your battery and your energy usage. A larger battery will provide more power for a longer period. It is recommended that you discuss your energy needs with your installer to determine the size of the battery you need for your home.
E. Do solar panels and battery storage save money?
Yes, solar panels and battery storage can reduce energy bills significantly, in some cases. By generating your own electricity, you can reduce your reliance on the grid and lower your energy bills. The amount you save will depend on the size of your solar panel system, your energy usage, and the cost of electricity in your area.
In some cases, our customers find that their energy accounts are in credit at the end of their first full year following solar panel and battery installation.
F. Can batteries be fitted to existing solar installations?
Yes. There are various methods of retrofitting battery storage. In some cases, an additional inverter will be required. This is referred to as AC coupling. If you already have a hybrid inverter, you may not need an additional inverter. As discussed in more detail in section IV.D, there are several considerations for installing battery storage alongside existing solar panel systems that benefit from Feed in Tariffs. It is crucial to ensure that any additions do not contravene the terms of your FIT contract.
iJo Power are able to advise on the particular design considerations based on your existing system.
F. Do solar panels add value to my home?
Yes, solar panels can add value to your home. A study by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory found that homes with solar panels sell for an average of 4% more than homes without solar panels. In addition, a solar panel system can make your home more attractive to buyers who are interested in eco-friendly features and lower energy bills.
If you would like answers to other frequently asked questions, head over to our extensive list of FAQs.
VII: Conclusion
A well-planned and installed solar battery system can offer long-lasting benefits, both environmentally and financially. By understanding the various aspects of sizing, purchasing, installation, and maintenance, you can confidently invest in a solar battery system that suits your needs and maximises your return on investment.
If you have any questions or would like to speak to a technical expert about your solar panel battery storage project, please get in touch with us at iJo Power.